Technology has helped to maintain the health of millions of patients worldwide. One of the most significant and relatively inexpensive forms of technology to revolutionise and innovate health has been the smartphone.
Smart handsets are at the forefront of development in low, middle and high-income countries. Together with falling handset prices and the United Nations’ promise to increase internet access in developing countries by 2020, it has created life changing possibilities for smartphone capabilities.
In different parts of the world, smartphones have already improved doctor-patient interaction. They have increased and enhanced care for patients while simultaneously reducing costs. The lives of people in developing countries are being ameliorated by the use of smartphone technology to aid healthcare, and this is how:
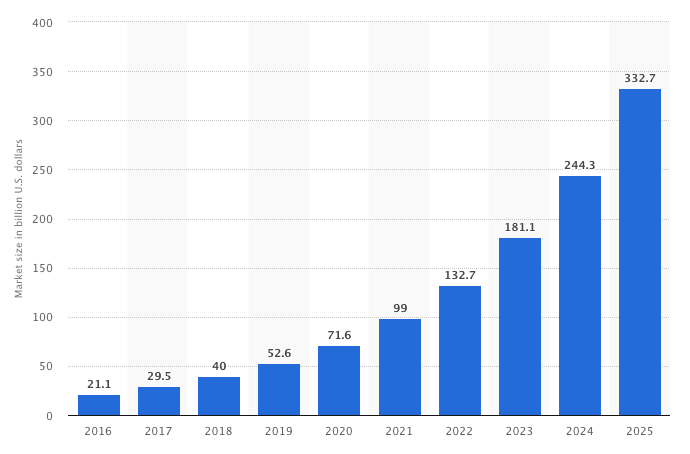
The graph above provided by Statista shows how influential the mobile health market is globally and how much it is projected to grow over the coming years.
Improving training and communication for Healthcare Professionals
Smartphones enable quicker communication between health services and encourage doctors to collaborate. Over the years we have seen rapid developments in cloud-based storage systems which help to promote collaboration and sharing of files, especially on mobile devices. This is because the nature of working with mobile technology means healthcare professionals have instant access to images and test results whenever and wherever they require them.
The use of Social networking can have significant advantages on the improvement of care as it is capable of connecting doctors, students and patients on a global scale. Together they can collaborate and share knowledge as well as give feedback, increasing healthcare and awareness of developments in care or diseases.
Using smartphones and tablets when training doctors and nurses can help an increasing number of healthcare professionals and improve communication between them. The significance and importance of technologies like smartphones in our lives mean they now play a vital role in our lifestyles. And so, incorporating it into the training of medical professionals can improve their skill set. They can be used to train healthcare professionals in low and middle- income countries, allowing them to gain greater access to tools. The advantage of this will see a greater number of doctors and nurses being trained on a large geographical scale in developing countries that need it the most. The outcome of this will mean better care for patients globally.
The advantages of e-learning and cloud-based technologies, along with social networking, help to facilitate the training of medical professionals. As mentioned above, they improve communication which effectively speeds up administration. This not only improves services for the patient, but it also means it does not involve patient participation or the need to interact with them.
Collaboration to improve care
Smartphone technology and other devices such as wearables are also helping to aid patient management. Patients can use smartphone apps to help them better manage their conditions. Dementia apps, for example, can use GPS signals to help family members keep track of their loved ones. They also help to collate vital information for healthcare professionals, allowing them to monitor how a patient’s condition has changed over time. They can use the data from the app to measure the patient’s performance to notice if medication or care needs be tailored or altered to suit the patients needs better. As patients get older and time goes on, their needs change. Smartphone apps can help identify how best to help.
As technology advances, we have seen other devices come to market, which can also help manage conditions. Smartwatches can continuously measure and passively monitor blood pressure and other vitals like heart rate. These can help patients with high blood pressure or heart problems. There is a range of wearable devices that have taken to the healthcare market, these include contact lenses which can measure glucose levels and eye pressure along with necklaces which can provide 24-hour ECG monitoring.
Smartphones and wearable devices give patients greater control over their health and the investigations into them. Smartphones help patients track their health and enhance their doctor-patient relationship by giving them better control. The patient will be able to understand their condition better, which means they will be able to decide on better care for themselves. They help the patients feel empowered about their conditions and encourage shared decision-making, which can also lighten the load for doctors.
Reducing costs for healthcare
Smartphone technology is inclusive and adaptable, which makes it perfect for use in developing countries. Although much of the high-end technology is indeed aimed at higher-income countries there is a wide range of devices that don’t meet the top tier specification levels but are just as good, and these are the devices that developing countries are using. They can keep up with innovations through creative ways by creating portable diagnostic devices that can measure a range of different metrics enabling doctors to diagnose and treat patients with chronic illnesses at the point of care. This is incredibly important in developing countries as environmental issues, and lifestyles mean sanitation and cleanliness is an issue.
The constant development of the smartphone and its intuitive nature can positively encourage innovation. As the smartphone develops, the technology used in them can be altered and used to create new devices. The upside to this is that the technology is already established, which rapidly reduces costs instantly. Still, we can use this as an opportunity to take technology from one device and work into another to progress another industry.
Complications
Although using smartphones for healthcare sounds excellent, there are some complications. Firstly, everyone is focused on developing an app which means there are such a large number of apps available for one condition. This makes it hard to know which ones to trust and which ones not to.
There is also plenty of room for error. Technology, although great, can sometimes let us down and put us in difficult situations. Connections are not always great and can drop from time to time. One of the biggest concerns when using devices is that there should be rigorous security checks in place to uphold patients right to confidentiality. Information shared across platforms over devices are subject to hackers. Patient details need to be held and stored in confidential settings keeping them secure.
Other complications that can arise from using smartphones can centre around the fact that not all forms of technology are compatible in different continents. This can make training and communication between professionals hard.
Although some challenges still need to be taken into consideration, the effects of smartphones on healthcare in developing countries appear to be considerably positive. Its implementation has the potential to transform and change healthcare in challenging areas. The smartphones ever-expanding attraction and influence can enable it to become the future of health.